Finding the right e-liquid is really important to make sure you get the best possible vaping experience. In this post we will be giving some pointers on how to identify the right vape juice to suit both you and your device.
Choosing the right nicotine strength
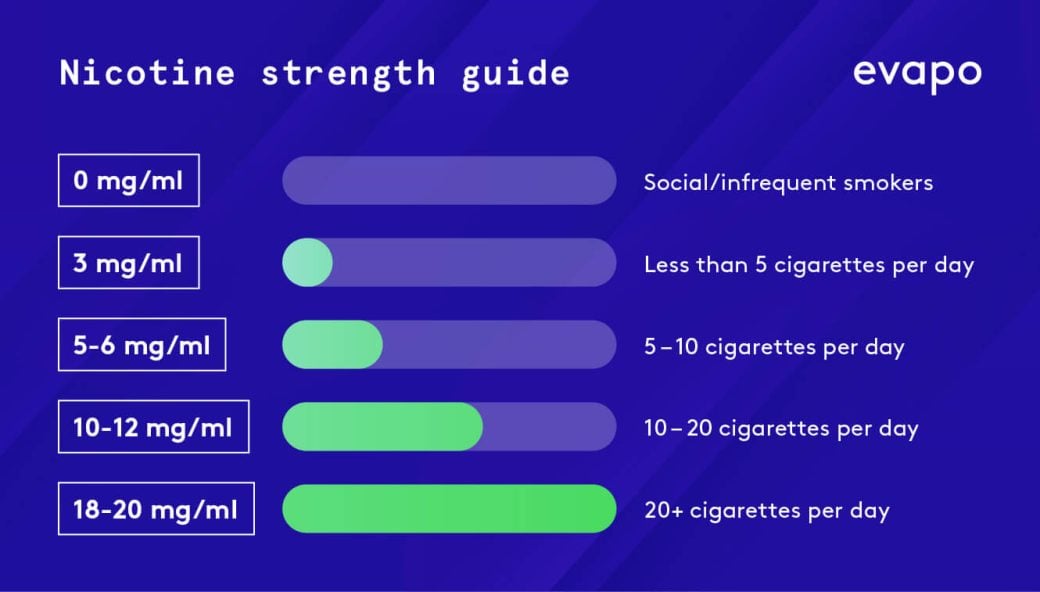
E-liquids are available in a range of different strengths that allow you to choose the specific one that best reflects your previous nicotine intake from smoking. What nicotine strength you choose depends largely on your previous smoking habits. As a general rule, we suggest the following:
- Heavy smoker - 20+ cigarettes a day: 18mg – 20mg
- Moderate smoker – 10 - 20 cigarettes a day: 10mg – 12mg
- Light smoker – 5 - 10 cigarettes a day: 6mg
- Casual smoker – Smokes few cigarettes or not every day: 0mg – 3mg
There may be some trial and error, if you are using an e-liquid and feel that the nicotine strength is too high or low try the next strength to see if it is more suitable.
You should also consider the type of nicotine in your e-liquid. Freebase nicotine is known for the ‘throat hit’ it offers, which to some makes it feel more like smoking, but others may find too harsh. If you feel the nicotine strength is correct but find the inhale is not comfortable try nic salt e-liquids, as they have a much smoother inhale even at high nicotine strengths.
Once you have been vaping for some time you may want to decrease your nicotine intake, by slowly dropping down to a lower strength over time, eventually getting to a nicotine free e-liquid. This is a personal preference, and you should only drop your nicotine strength if you feel you are ready. You can read more about this in our blog post ‘How to decrease your nicotine strength’.
Why is choosing the right nicotine strength important?
Finding the right nicotine strength is a really important part of making the switch from smoking to vaping. E-cigarettes are designed to be an alternative nicotine source for use as a stop smoking aid, to help keep nicotine cravings at bay and give you the best chance at a successful stop smoking attempt.
Nicotine is the addictive substance in cigarettes and is responsible for the unpleasant withdrawal that many people experience when they make a stop smoking attempt. Using an e-cigarette can help manage nicotine cravings, but if you choose a nicotine strength that is too low it may not fully satisfy your nicotine cravings, and this can make it harder to stay away from cigarettes.
On the other hand, choosing a nicotine strength that is too high can cause headaches and nausea, as you are introducing more nicotine into your system than your body is used to.
Choosing the right e-liquid ratio
Vegetable glycerin (VG) and propylene glycol (PG) are the two base ingredients for e-liquids. In e-liquids they are both used as diluents, substances used to dilute the flavourings and nicotine to produce an overall consistency that is right for vaping. Both VG and PG are common ingredients in a number of food, cosmetic and pharmaceutical products. VG is the ingredient in e-liquids that is responsible for creating the vapour, and PG is used as a carrier for flavourings and nicotine to make sure they are evenly distributed throughout the e-liquid.
E-liquids are available with different ratios of VG and PG to make them suitable for use in different types of vape kits.
50/50 e-liquids
50/50 e-liquids contain an equal amount of VG and PG and are ideal for use with starter kits and pod systems. These types of devices tend to have small coils which can easily absorb the thin consistency of a 50/50 vape juice. 50/50 e-liquids also tend to be available in a wider variety of nicotine strengths than high VG e-liquids, allowing newer vapers to select the strength that best satisfies their nicotine cravings.
Who Should Use A 50/50 E-liquid?
Generally, the majority of starter kits with a mouth to lung draw will work best with a 50:50 ratio e-liquid.
There are some exceptions, anything with a sub-ohm tank, but for the most part starter kits contain a small coil that will best absorb a thinner consistency liquid like a 50:50 or even a 60:40 high PG.
This is also the case with pod systems and clearomiser style devices. 50:50 e-liquids tend to be more suited towards new vapers because they give a bit more of a throat hit which can feel more similar to smoking than the smoothness of a high VG liquid, and they also tend to offer a wider range of nicotine strengths.
High VG e-liquids
High VG e-liquids contain more VG than PG, most commonly with a 70/30 ratio, making for a thicker consistency. These e-liquids are perfect for use with advanced vape kits and sub-ohm devices, which tend to have larger coils with more exposed cotton. These bigger coils can easily absorb the thicker e-liquid without becoming over saturated and leaking. High VG e-liquids also create more cloud production, perfect for cloud chasers and high wattage devices.
When selecting an e-liquid it is important to consider the type of device you are using to ensure a pleasant vaping experience and help your coils last as long as possible. If you are using a starter kit or pod system with a small coil and select a high VG e-liquid, you may find that the coil burns out prematurely or you get dry hits, as the smaller coils cannot absorb the thicker e-liquid easily. On the other hand, if you are pairing a more advanced vape kit with a 50/50 e-liquid, you may experience leaking and spitting. This is because the thinner e-liquid is very easy for the large coils to absorb, making then become over saturated, and the excess e-liquid will start to escape through the airflow and mouthpiece.
Who Should Use A High VG E-Liquid?
High VG e-liquids are ideal for anyone using a sub-ohm tank or most kinds of rebuildable atomisers. Because these tend to have a direct to lung draw and produce a lot more vapour, they better suit the smoothness and cloud production of a high VG liquid.
For the most part, high VG e-liquids come in a wide variety of flavours and are often available in shortfills, however, the range of nicotine strength available is often limited and you will rarely find a high VG liquid in a higher strength than 6mg.
Choosing the right e-liquid flavour for you
Finally, finding a flavour you love is not just about making vaping more enjoyable, it also makes you more likely to stick to vaping if you enjoy the flavour, and less likely to return to smoking. Which flavour will work best for you is highly personal and depends entirely on your own personal preferences.
While e-cigarettes are designed as an alternative to smoking, many people find they prefer using a non-tobacco flavoured e-liquid. If you think about it, most people do not smoke for the flavour. Some people do like the familiar taste of tobacco flavoured e-liquids, but other flavours like menthols and fruit flavours tend to be the more popular choice. A good place to start is to go for flavours that reflect foods and drinks you like, such as your favourite fruit or dessert. There are countless flavours available, and don’t be afraid to try a few. Some vapers find a flavour they love and will continue to use it all the time, but others will rotate between different flavours to keep things interesting.
What is in my e-liquid?
As mentioned above, e-liquids contain VG and PG which are used to dilute the overall composition. Although VG and PG make up the bulk of an e-liquid, they are relatively flavourless and are used to dilute the flavourings and nicotine into a formula which can be safely vaped.
Nicotine
E-liquids can be purchased both with or without nicotine, so whether your vape juice contains any is entirely your choice.
Nicotine is a naturally occurring substance found in some of the plants in the Solanaceae family. This not only includes the tobacco plant, but many others such as aubergines and tomatoes. The tobacco plant is the richest source of nicotine, containing levels ranging from 8 – 14%.
Nicotine has a stimulant effect similar to that of caffeine and is an addictive substance, but is not responsible for causing any forms of cancer. Nicotine is the addictive substance in cigarettes and is used in e-liquids to help those who are making the switch from smoking to vaping transition to a less harmful source of nicotine.
Nicotine is extracted from the tobacco leaf through a chemical process which results in a pure, liquid form of nicotine. This liquid form is known as freebase nicotine and when vaping first rose in popularity this was the most common form of nicotine found in e-liquids. It is an alkaline with a pH of around 8 and the alkaline nature is responsible for the ‘throat hit’ that many vapers associate with freebase nicotine e-liquids.
However, in recent years nicotine salt e-liquids have become the most popular and commonly available type of vape juice. They are made by adding an acid to freebase nicotine, which removes the nicotine salts and results in a form of nicotine with a pH of between 5 – 6. Nic salts are known for having a smoother inhale even at high nicotine strengths and absorbing quickly into the blood stream to satisfy cravings fast. We have lots more information about nicotine salt e-liquids in our blog post ‘What are nic salts? A comprehensive guide to using salt nicotine’.
Whether you are looking to get started with vaping and want some advice on what e-liquid you need or are an experienced vaper and just want to try something new, pop in to your local Evapo store or reach out to our Customer Service team and we will be happy to offer advice and recommendations.




























